In recent years, a sustainable agricultural practice has been gaining traction worldwide, promising to revolutionize soil health and carbon sequestration. This practice revolves around the production and application of biochar, a carbon-rich material derived from the pyrolysis of organic waste. From its humble origins, biochar has emerged as a potent tool in combating climate change while enhancing agricultural productivity. Let’s delve deeper into this fascinating phenomenon and explore its potential implications.
What is Biochar?
Biochar is a charcoal-like substance produced through biomass pyrolysis plant, such as wood chips, agricultural residues, or organic waste. Pyrolysis is a process that involves heating organic matter in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the decomposition of the material into volatile gases, bio-oil, and biochar. Unlike traditional charcoal production, which focuses on maximizing heat output, biochar production prioritizes the retention of carbon in the resulting material.
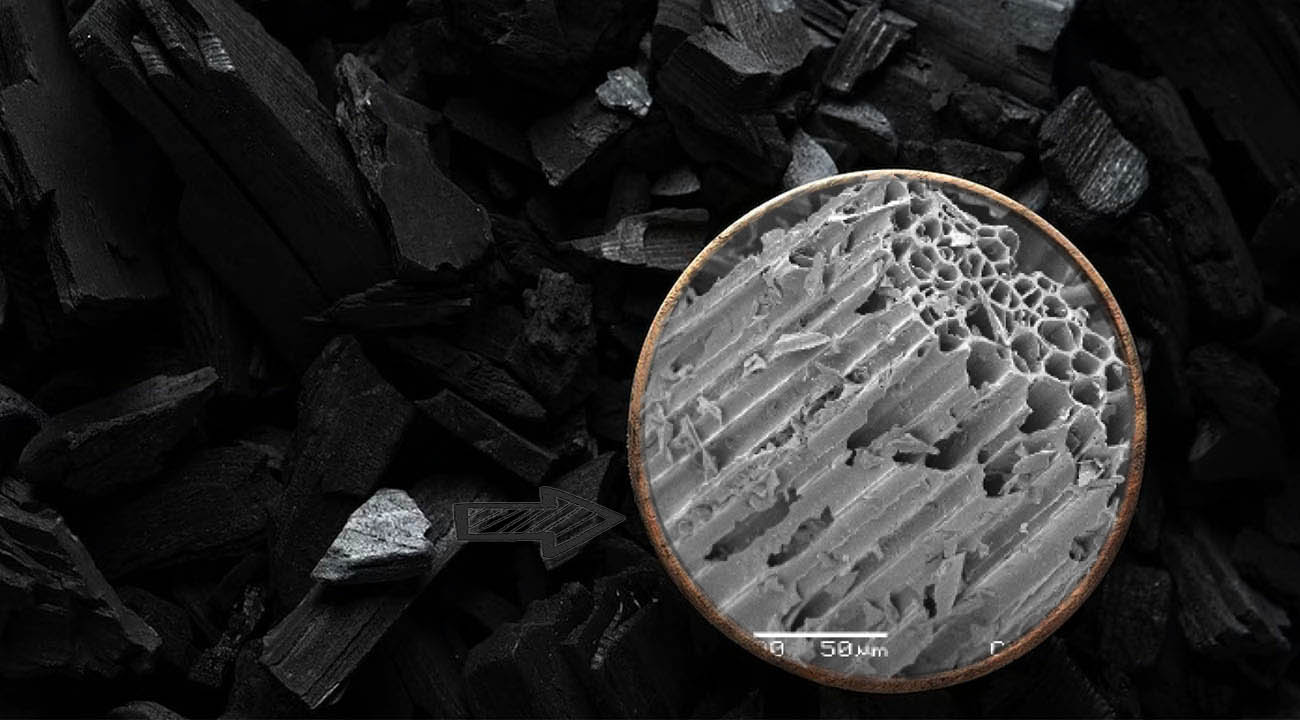

Soil Health Benefits
One of the most significant advantages of biochar from charcoal machine lies in its ability to improve soil health. When applied to agricultural soils, biochar acts as a stable carbon sink, sequestering carbon for hundreds to thousands of years. This not only helps mitigate climate change by reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels but also enhances soil fertility and structure.
Carbon Sequestration
The carbon-rich nature of biochar makes it an effective means of carbon sequestration. By incorporating biochar into soil, carbon is stored in a stable form, preventing it from being released back into the atmosphere as greenhouse gases. Studies have shown that biochar-amended soils can sequester significant amounts of carbon, making them valuable allies in the fight against climate change.
Soil Fertility
Biochar also improves soil fertility by enhancing nutrient retention and availability. Its porous structure provides habitat for beneficial microbes and fungi, promoting nutrient cycling and improving soil structure. Additionally, biochar can adsorb and retain water and nutrients, reducing leaching and runoff and ensuring their availability to plants over time.
Remediation of Contaminated Soils
In addition to its benefits for agricultural soils, biochar has shown promise in remediating contaminated soils. Its high surface area and porosity allow it to adsorb heavy metals, pesticides, and other pollutants, reducing their mobility and bioavailability. This makes biochar a valuable tool for restoring degraded lands and mitigating the impacts of industrial activities.

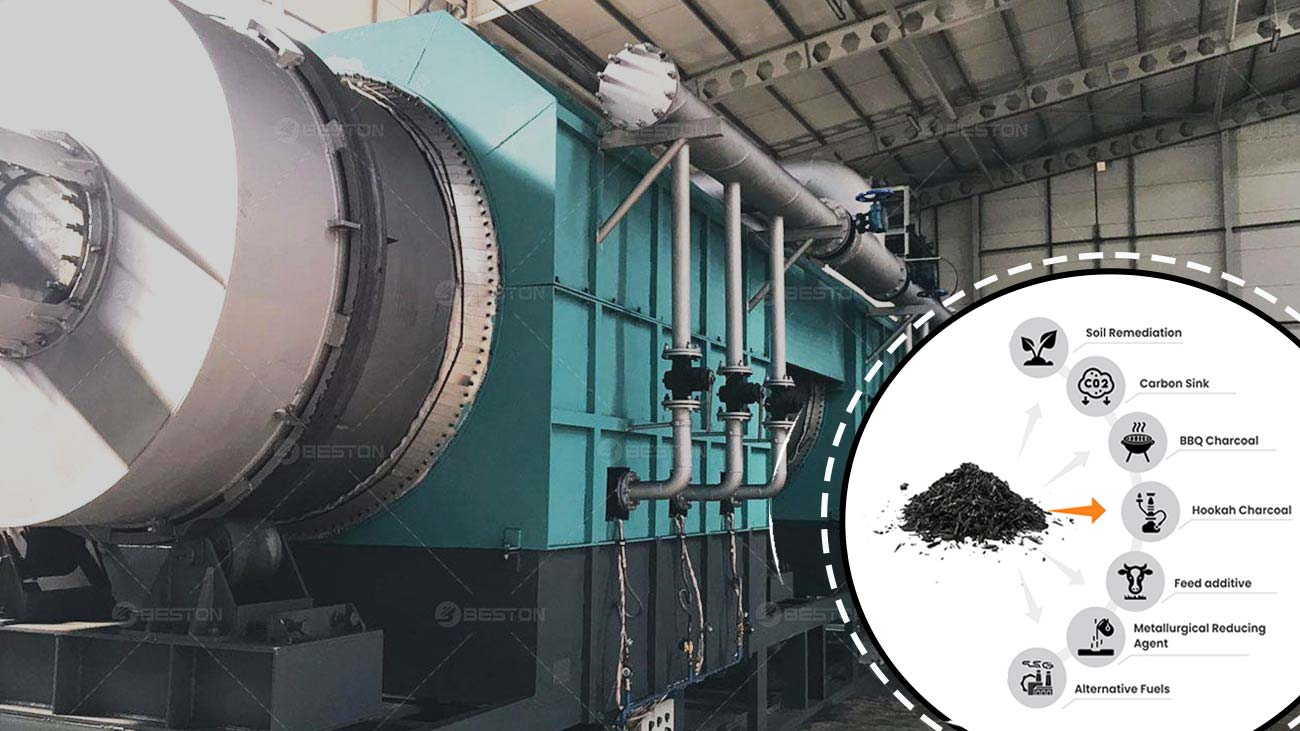
Applications of Biochar
The versatility of biochar produced by biochar production equipment extends beyond agriculture, with various applications in environmental remediation, renewable energy, and sustainable development.
Waste Management
Biochar production offers a sustainable solution to the management of organic waste streams. By converting biomass into biochar through pyrolysis, organic waste can be repurposed into a valuable soil amendment, reducing the burden on landfills and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from decomposition.
Renewable Energy
The byproducts of biochar production, such as bio-oil and syngas, can be utilized as renewable energy sources. Bio-oil can be refined into biofuels, while syngas can be used for heat and power generation. This integrated approach to biomass utilization maximizes resource efficiency and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Climate Change Mitigation
Biochar plays a crucial role in climate change mitigation efforts by sequestering carbon and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Its adoption in agriculture and other sectors can contribute to achieving carbon neutrality and meeting emissions reduction targets set forth in international agreements such as the Paris Agreement.
Contact Beston Group
Interested in learning more? Head over to Beston Group for a detailed overview.